What is Scabies?
Written By Vishwjeet Singh, July 27, 2020
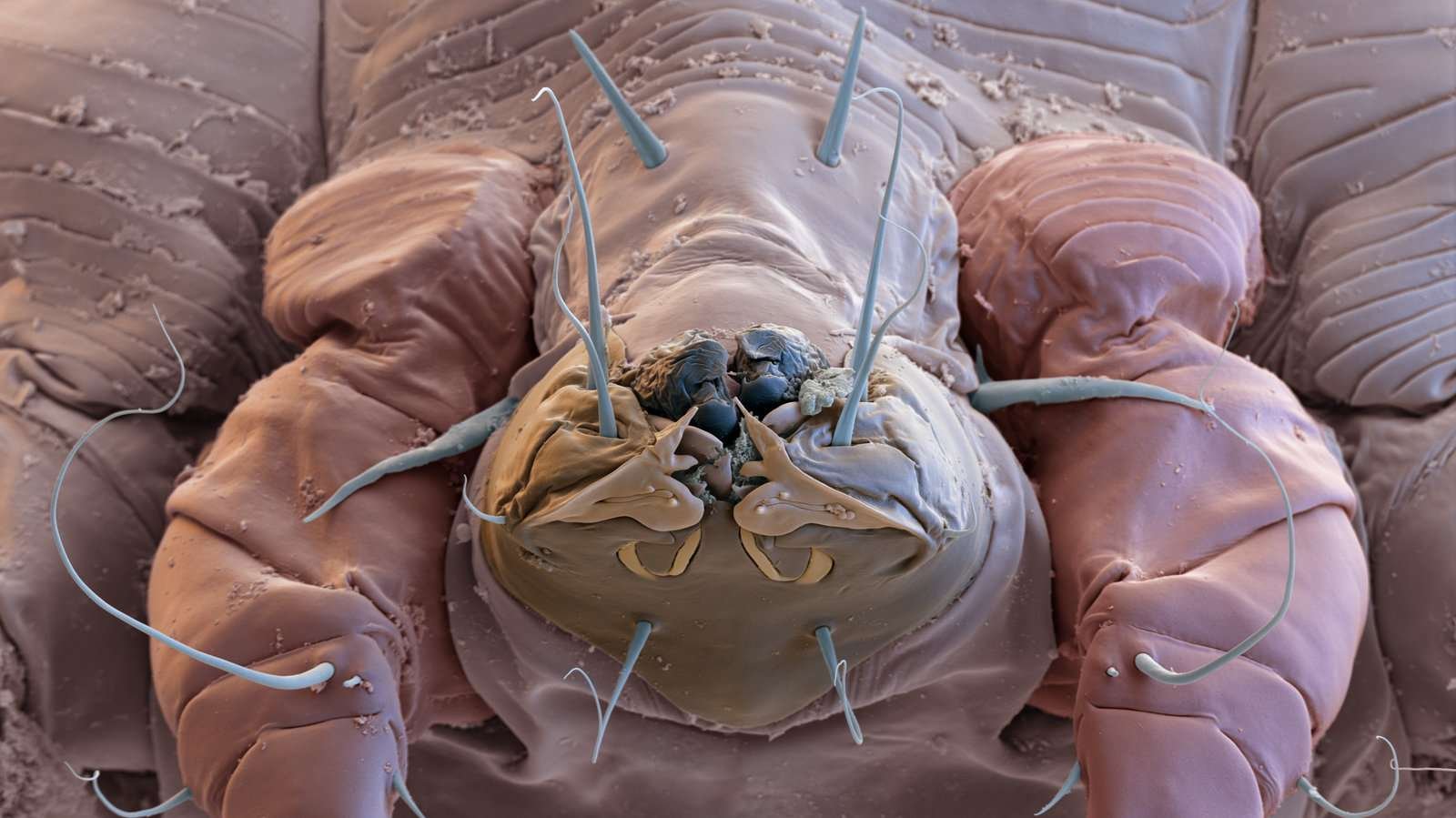
Scabies is a skin infestation caused by a mite known as the Sarcoptes scabiei. Untreated, these microscopic mites can live on your skin for months. They reproduce on the surface of your skin and then burrow into it and lay eggs. this causes itching and red rashes on the skin. the most common symptoms of scabies are intense itching and a pimple-like skin rash. The scabies mite usually is spread by direct, prolonged, skin-to-skin contact with a person who has scabies. Scabies occurs worldwide and affects people of all races and social classes. Scabies can spread rapidly under crowded conditions where close body contact is frequent. When a person is infested with scabies mites the first time, symptoms usually do not appear for up to two months (2-6 weeks) after being infested; however, an infested person still can spread scabies during this time even though he/she does not have symptoms.
What are the Symptoms of Scabies?
The most common symptoms of scabies, itching, and a skin rash, are caused by sensitization to the proteins and faeces of the parasite. Severe itching (pruritus), especially at night, is the earliest and most common symptom of scabies. A pimple-like (papular) itchy (pruritic) “scabies rash” is also common.
Common sites for scabies in older children and adults include the:
- Between the fingers
- Wrist
- Elbow & Armpit On the inner elbows
- Penis
- Nipple
- Waist
- Buttocks
- Shoulder blades
- Along the insides of the wrists
- On the soles of the feet
- Around the breasts
- Around the male genital area
- On the buttocks
- On the knees
- Around the waistline and navel
In infants and young children, common sites of infestation usually include the:
- Scalp
- Palms of the hands
- Soles of the feet
- Head
- Face
- Neck
- hands
What are the causes of scabies?
The eight-legged mite that causes scabies in humans is microscopic. The female mite burrows just beneath your skin and makes a tunnel where it deposits eggs. The eggs hatch and the mite larvae work their way to the surface of your skin, where they mature and can spread to other areas of your skin or to the skin of other people. The itching of scabies results from your body’s allergic reaction to the mites, their eggs, and their waste. Close physical contact and, less often, the sharing of clothing or bedding with an infected person can spread the mites. Animals and humans all are affected by their own distinct species of mites. Each species prefers one specific type of host and doesn’t live long away from that preferred host. Humans may have a temporary skin reaction from contact with the animal scabies mite. But people are unlikely to develop full-blown scabies from this source, as they might from contact with the human scabies mite. Female mites will lay eggs. Your skin will react to the mites and their waste, and you’ll develop a red, itchy rash.
These mites are easily passed between people. Direct skin-to-skin contact is the most common way to share the infestation. The mites can also be spread through infested:
- furniture
- clothes
- bedding
Facilities where people live in close contact to one another often see infestations spread easily. These may include nursing homes or extended-care facilities.
Anyone can get scabies, but those at higher risk include:
- Sexually active adults
- Prison inmates
- People in institutional care
- People living in crowded conditions
- People in child care facilities
Can You Get Scabies From a Pet?

Dogs and cats get scabies, too — better known as mange. However, canine scabies and feline scabies are not caused by the same type of mite that triggers human scabies. You can get mites from handling an infested pet, but these mites can’t reproduce in human skin. This means they usually die off without causing serious symptoms.
What are the Preventions of Scabies?
To prevent re-infestation and to prevent the mites from spreading to other people, take these steps:
- Clean all clothes and linen. Use hot, soapy water to wash all clothing, towels, and bedding used within three days before beginning treatment. Dry with high heat. Dry-clean items you can’t wash at home.
- Starve the mites. Consider placing items you can’t wash in a sealed plastic bag and leaving it in an out-of-the-way place, such as in your garage, for a couple of weeks. Mites die after a few days without food.
What are the complications of scabies after being infected?
The intense itching of scabies leads to scratching that can lead to skin sores. The sores sometimes become infected with bacteria on the skin, such as Staphylococcus aureus or beta-hemolytic streptococci. Sometimes the bacterial skin infection can lead an inflammation of the kidneys called post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis.
There are some groups that are on the high risk of getting complicated health issues –
* People with chronic health conditions that weaken the immune system, such as HIV or chronic leukemia
* People who are very ill, such as people in hospitals or nursing facilities
* Older people in nursing homes
What are the treatment methods for Scabies?
here are some treatments methods that can help you in getting rid from scabies
Tea tree oil
Small studies show tea tree oil may treat scabies, while also easing itching and helping eliminate the rash. However, it won’t work well on mites that are burrowed into your skin.
Aloe vera
This gel is known for its ability to ease skin irritation and burning, but a small study found that aloe vera was just as successful as a prescription treatment at treating scabies. Just be sure to buy pure aloe vera, not an aloe vera-infused product.
Capsaicin cream
Though it will not kill the mites, creams made with the capsaicin from cayenne peppers may relieve pain and itching by desensitizing your skin to the bothersome bites and bugs.
Essential oils
Clove oil is a natural bug killer, so it stands to reason mites might die in its presence. Other essential oils, including lavender, lemongrass, and nutmeg, could have some benefit at treating scabies.
Soaps
Active components from the bark, leaves, and seeds of the neem tree may kill the mites that cause scabies. Soaps, creams, and oils made with the tree’s extract may help deliver the fatal blow to the mites.
Some doctors also prescribe the antibacterial soaps that can kill the bacteria but excess use of antibacterial soap can lead to some side effects.
How Soon Will Scabies Go Away?

Scabies medications can kill the mites and eggs quickly, and patients can usually return to school or work 24 hours after starting treatment. However, the itch may persist for a few weeks. This is the result of an ongoing allergic reaction in the skin. If the itching continues for more than four weeks or a new rash appears, see your doctor. It may be necessary to reapply scabies medication.
Microscopic Video of the Sarcoptes scabiei mite


