What is Cancer?
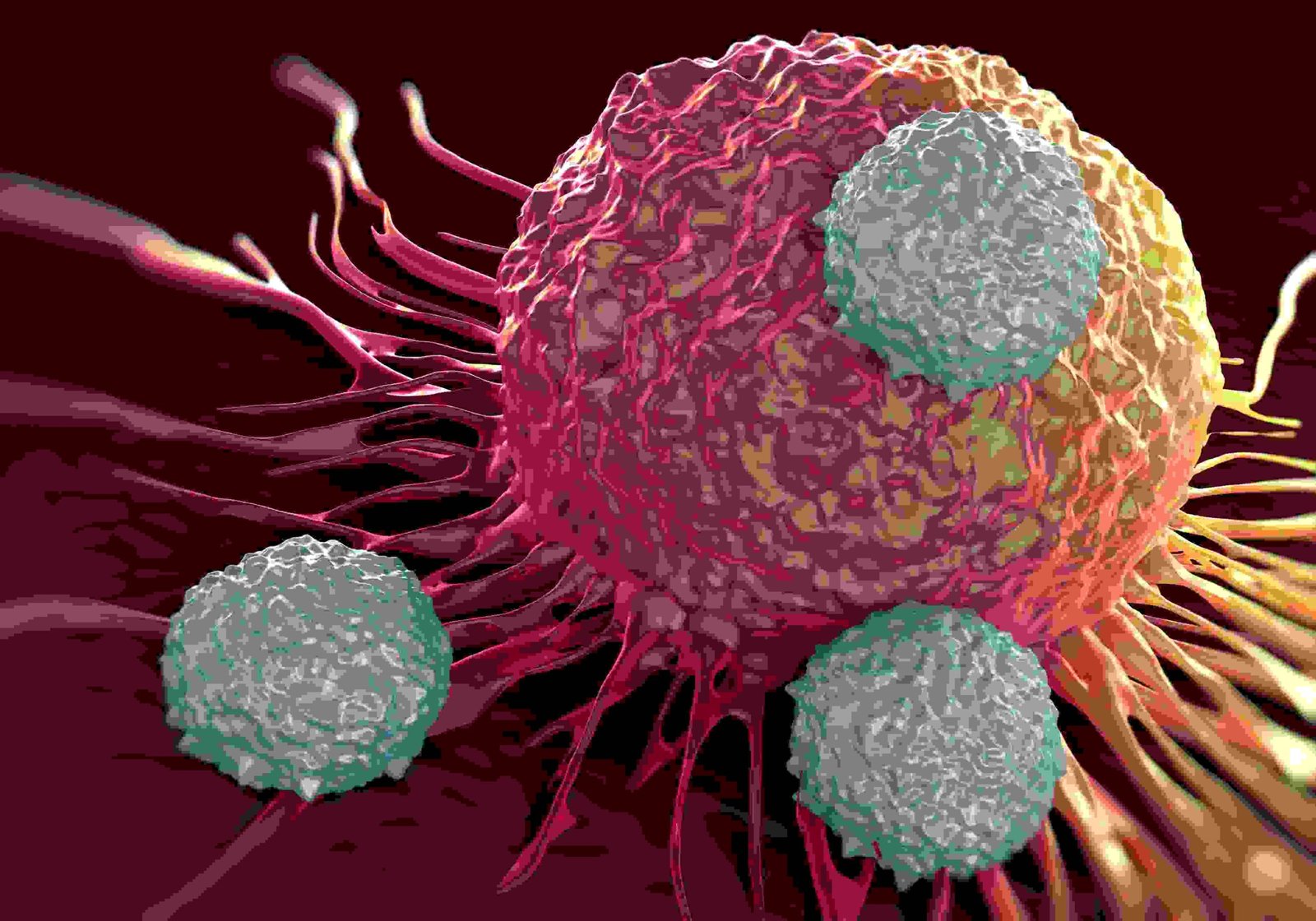
What is Cancer?
Cancer begins in your cells, which are the building blocks of your body. Cancer is the name given to a collection of related diseases. In all types of cancer, some of the body’s cells begin to divide without stopping and spread into surrounding tissues. Cancer, also called malignancy, is an abnormal growth of cells.
There are more than 200 types of cancer, including blood cancer, breast cancer, skin cancer, lung cancer, colon cancer, prostate cancer, and lymphoma. Most cancers are named for where they start. For example, lung cancer starts in the lung, and breast cancer starts in the breast. It can develop almost anywhere in the body. Cancer causes cells to divide uncontrollably. This can result in tumors, damage to the immune system, and other impairment that can be fatal. Between 30-50% of all cancer cases are preventable.
Healthy cells have a specific life cycle, reproducing, and dying off in a way that is determined by the type of cell. New cells take the place of old or damaged cells as they die. Cancer disrupts this process and leads to abnormal growth in cells. It’s caused by changes or mutations in DNA. Cancer is the second-leading cause of death in the world. But survival rates are improving for many types of cancer, thanks to improvements in cancer screening and cancer treatment.
What causes cancer?
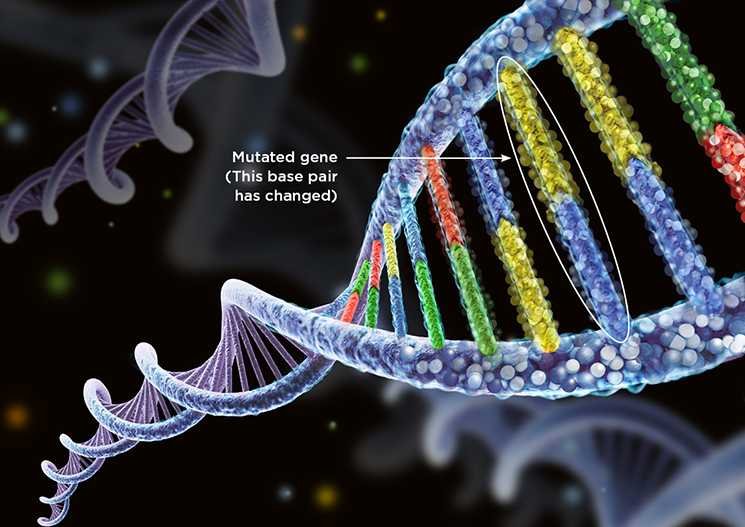
Cancer is a genetic disease—that is, it is caused by changes to genes that control the way our cells function, especially how they grow and divide. Most of the time, cells are able to detect and repair DNA damage. The DNA inside a cell is packaged into a large number of individual genes, each of which contains a set of instructions telling the cell what functions to perform, as well as how to grow and divide.
If a cell is severely damaged and cannot repair itself it undergoes so-called programmed cell death or apoptosis. Cancer occurs when damaged cells grow, divide, and spread abnormally instead of self-destructing as they should. There are many causes of cancer, and some are preventable such as a person can prohibit the use of tobacco, alcohol, etc etc.each person’s cancer has a unique combination of genetic changes. As cancer continues to grow, additional changes will occur. Even within the same tumor, different cells may have different genetic changes.
What are the types of cancer?
Doctors divide cancer into types based on where it begins. Four main types of cancer are:
- A carcinoma begins in the skin or the tissue that covers the surface of internal organs and glands. They are formed by epithelial cells, Carcinomas usually form solid tumors. They are the most common type of cancer. Examples of carcinomas include prostate cancer, breast cancer, lung cancer, and colorectal cancer.
- A sarcoma begins in the tissues that support and connect the body. this form in bone and soft tissues, including muscle, fat, blood vessels, lymph vessels, and fibrous tissue (such as tendons and ligaments). Osteosarcoma is the most common cancer of bone
- Leukemia is a cancer of the blood. Leukemia begins when healthy blood cells change and grow uncontrollably. The 4 main types of leukemia are acute lymphocytic leukemia, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, acute myeloid leukemia, and chronic myeloid leukemia. these groups based on how quickly the disease gets worse (acute or chronic) and on the type of blood cell the cancer starts in (lymphoblastic or myeloid).
- Lymphomas. Lymphoma is a cancer that begins in the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system is a network of vessels and glands that help fight infection. There are 2 main types of lymphomas: Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Hodgkin lymphoma – People with this disease have abnormal lymphocytes that are called Reed-Sternberg cells. These cells usually form from B cells.
- Non-Hodgkin lymphoma – This is a large group of cancers that start in lymphocytes. The cancers can grow quickly or slowly and can form from B cells or T cells.
There are many other types of cancer but mainly categorized into 4 types.
What are the risk factors for cancer?

Risk factors for cancer include:
- excess body weight
- physical inactivity
- poor nutrition
- inherited genetic defects (for example, BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations),
- infections,
- environmental factors (for example, air pollution), and
- poor lifestyle choices — such as smoking and heavy alcohol use — can also damage DNA and lead to cancer.
- Occupational carcinogens
- Exposure to different types of ionizing radiation from both man-made or natural radiation
What is carcinogens and how many types of they are?

A carcinogen is any substance, radionuclide, or radiation that promotes carcinogenesis, the formation of cancer. This may be due to the ability to damage the genome or to the disruption of cellular metabolic processes.
Three types of carcinogens are mainly considered as a cancer causing agents –
- physical carcinogens, such as ultraviolet and ionizing radiation;
- chemical carcinogens, such as asbestos, components of tobacco smoke, aflatoxin (a food contaminant), and arsenic (a drinking water contaminant); and
- biological carcinogens, such as infections from certain viruses, bacteria, or parasites.
What are the common sign & symptoms of cancer?

Knowing the signs and symptoms of cancer can help you and your doctor make a speedy diagnosis so that the cancer can be treated early.
Indications of cancer include such things as
- A thickening or lump in any part of the body
- unexplained weight loss,
- fever and night sweats,
- unexplained bleeding or discharge
- A sore that does not heal
- Hoarseness or a cough that does not go away
- A hard time swallowing
- Discomfort after eating
- Changes in bowel or bladder habits
- Unusual bleeding
- Feeling weak or very tired
None of these signs should cause immediate concern; they don’t always mean you have cancer. Some of them can be caused by entirely unrelated ailments
How cancer is diagnosed?

Most cancers are initially recognized either because of the appearance of signs or symptoms or through screening. Neither of these leads to a definitive diagnosis, which requires the examination of a tissue sample by a pathologist.
And your doctor can perform some tests for determining the severity of cancer such as
Physical exam: During a physical exam, he or she may look for abnormalities, such as changes in skin color or enlargement of an organ, that may indicate the presence of cancer.
Laboratory tests: such as urine and blood tests
Imaging tests: Imaging tests used in diagnosing cancer may include a computerized tomography (CT) scan, bone scan, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), positron emission tomography (PET) scan, ultrasound, and X-ray, among others.
Biopsy: During a biopsy, your doctor collects a sample of cells for testing in the laboratory. Normal cells look uniform, with similar sizes and orderly organization. Cancer cells look less orderly, with varying sizes and without apparent organization.
How is cancer treated?

Treatment options depend on the type of cancer, its stage if the cancer has spread, and your general health. The goal of treatment is to kill as many cancerous cells while reducing damage to normal cells nearby. Advances in technology make this possible.
Surgery
The goal of surgery is to remove cancer or as much cancer as possible.
Chemotherapy
Uses medications that are toxic to cells to kill rapidly dividing cancer cells.
Radiation Therapy
Uses powerful, focused beams of radiation inside (brachytherapy) or outside (external beam radiation) your body to kill cancer cells.
Stem Cell (Bone Marrow) Transplant
Repairs diseased bone marrow with healthy stem cells. Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that can have a variety of functions. These transplants allow doctors to use higher doses of chemotherapy to treat cancer.
Immunotherapy (Biological Therapy)
Uses antibodies to help your body’s immune system recognize cancer so it can fight it off.
Hormone therapy. Some types of cancer are fueled by your body’s hormones. Examples include breast cancer and prostate cancer. Removing those hormones from the body or blocking their effects may cause the cancer cells to stop growing.
Targeted drug therapy. Targeted drug treatment focuses on specific abnormalities within cancer cells that allow them to survive.
Alternative Medicine
Used to decrease symptoms of cancer and side effects of cancer treatment, such as nausea, fatigue, and pain. Alternative medicine includes:
- acupuncture
- hypnosis
- massage
- yoga
- meditation
- relaxation techniques
Clinical trials. Clinical trials are studies to investigate new ways of treating cancer. Thousands of cancer clinical trials are underway
The same cancer type in one individual is very different from that cancer in another individual. Within a single type of cancer, such as breast cancer, researchers are discovering subtypes that each requires a different treatment approach.



Hi there mates, pleasant article and nice urging commented at this place, I am actually enjoying by these. Heda Lamar Croft
Thankfulness to my father who shared with me regarding this webpage, this weblog is in fact awesome. Hedwig Carver Glassman
I truly appreciate this post.Really looking forward to read more. Much obliged. Marion Tomasic