Monofilament Test For Neuropathy: How To Use And More
People can develop a risk of nerve damage called peripheral neuropathy. This is a condition that affects your feet and hands. You may feel pain, burning, tingling, or lose all sensation in these body parts. Nerve damage makes you unable to feel any injury. It can be a huge problem, as a small cut can get infected easily if unnoticed. Severe infection can lead to foot ulcers and amputations. So, diagnosing and treating neuropathy issues can help protect yourself, and here, the monofilament test has a crucial role. Doctors perform this test once a year using a monofilament(a fiber), which helps check the loss of sensation in the body parts. Let’s understand thoroughly about this testing, how it is performed, and how it supports treating peripheral neuropathy.
What Is a Monofilament Test?
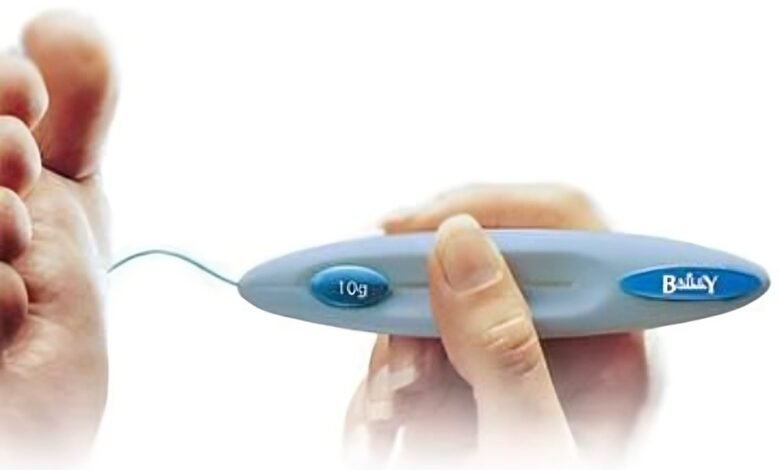
A monofilament testing, typically known as Semmes Weinstein monofilament test (SWM), is performed to test for neuropathy by healthcare providers. It helps check the sensation in your feet, hands, fingers, or toes. In this accessible yet sensitive analysis, doctors use monofilament, a piece of fiber attached to the plastic base that looks like a fishing line and touches against the surface of your hands or feet’s skin. By doing this, your ability to feel that fiber is examined. If you can not sense any action, it points out that there is nerve damage in that body part. Sometimes, the monofilament testing is also called the 10-gram monofilament test, as fiber is adjusted to bow down to 10 g of pressure. As monofilament testing is used for detecting neuropathy in people, you might be wondering what this condition is and its symptoms and causes. Below, we have explained in detail!
What Is Peripheral Neuropathy And Its Symptoms?
Peripheral neuropathy is typically a condition that happens when the peripheral nerves get damaged. This causes weakness, pain, and numbness in the hands and feet. In addition, it can impact the other areas and functioning of the body, including urination and digestion. The symptoms of neuropathy include:
-
Tingling or burning sensation
-
Temporary or permanent numbness
-
Dysfunction in body organs or glands
-
Increase in sensitivity to touch
-
Muscle weakness or muscle wasting
-
Problems with sexual and urination function
-
Problem emptying the bladder fully
-
Paralysis
-
Pain
Causes Of Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy can occur due to several factors or underlying health conditions. These include:
Diabetes
Studies have shown that diabetes is the most common cause of peripheral neuropathy in the United States, around 83%. Unmanaged Type 2 diabetes (increased levels of blood glucose) in the long term can lead to peripheral nerve damage, causing extreme pain, numbness, and loss of sensation in the feet and lower legs. You can prevent neuropathy caused by diabetes, which is also called diabetic peripheral neuropathy, by monitoring your blood sugar levels, checking your feet for signs of infection or injuries, and discussing symptoms of neuropathy with doctors to get early and effective treatments.
Injury
Injuries to the peripheral nerve can happen directly from physical trauma. Those can include fractures, car accidents, or accidental falls. Also, inactivity, swelling, stretching, and holding still in one position for too long can cause nerve damage. This type of damage occurs in one area and can be long-term or even, in some cases, permanent. According to research, some patients experience mild and slow progressive finger tingling due to the increased pressure in the median nerve in the wrist. This condition is called carpal tunnel syndrome.
Vitamins Deficiency
Deficiency of certain vitamin types, including vitamins B1, B6, B9, B12, B9, and E, can develop peripheral nerve damage. Studies show that among 2287 older people, 7% of people were found with B12 deficiency. The deficiency of this vitamin type was linked to motor and sensory peripheral nerve function. This condition leads to injuries in the myelin sheath, a layer that covers and protects nerves from any damage. Without this protective sheath, the nerves can not function properly.
Medications
Medication can also be the reason for peripheral neuropathy. Those medicines can be some blood pressure medications, chemotherapy drugs for cancer treatment, anticonvulsants to treat seizures, or drugs to prevent bacterial infections. Though there is no evidence found that can confirm that statins, a type of drug used to prevent cardiovascular disorders or reduce cholesterol levels, can cause neuropathy, they can increase the risks of developing neuropathy from other factors.
Note: If the risk of neuropathy is higher if you have diabetes, doctors will recommend a diabetic foot exam more than one time annually. What is a diabetic foot exam? Below is a complete explanation!
What Is A Diabetic Foot Exam?
Here is the comprehensive diabetic foot exam documentation that can provide detailed information on diabetic foot exams. This type of examination can help test for neuropathy in the feet of patients with diabetes. Diabetic foot issues can occur due to damage in the blood vessels and nerves of the feet due to increased blood sugar levels. This kind of nerve damage caused by diabetes is also called “diabetic neuropathy,” making the feet feel tingling or numb and leading to loss of sensation in the feet. You may also notice callus, cuts, or even blisters in the foot, which, if left untreated, can become infected ulcers and can cause gangrene. Here, diabetic foot exams play a role.
In diabetic foot exams, doctors examine you physically by checking your tendon reflexes, muscle tone, strength, sensitivity to pain, touch, vibration, and temperature. They also review your medical history, including the medicines you take to manage diabetes and other health issues and the symptoms you may have. Moreover, they check the nerve functions through a monofilament exam, which quickly identifies nerve damage or loss of sensation in the feet. Wondering how the monofilament foot exam helps diagnose diabetic neuropathy. Read on!
How To Use Monofilament Test For Diabetic Foot Exam
These are the monofilament test steps that you can follow for diabetic foot test:
-
Firstly, touch the monofilament to the sensitive part of the feet so the patients know how they should feel.
-
Use the monofilament to test the five spots of both feet. Those include 1st, 3rd, and 5th metatarsal heads, Plantar hallux(big toe) surface, and 3rd toe. If a callus is formed in these sites, apply the monofilament at the nearest non-calloused areas.
-
Ask the patients to close their eyes and reply “Yes” whenever they feel the touch on any part of their feet.
-
Hold the monofilament perpendicular(90 degrees) to the skin’s surface.
-
Gently push the monofilament till it is bent to 1 cm.
-
Keep the monofilament in the same position for about 1 to 2 seconds. Next, slowly release the pressure until it lifts from the skin’s surface.
-
Remove the contact of monofilament from the skin.
-
Never use fast movement. The skin contact, approach, and release of the monofilament from the skin surface should be around 1½ seconds.
-
If the patient does not react to touching the given site of the feet, repeat the test on another area. Even if there is no reaction, record it as a negative review.
-
The maximum monofilament test scoring is 10. A score of 8 and below this range indicates neuropathy(nerve damage) in feet.
-
Note that: Always replace the monofilament after using it 500 times.
However, doctors can also recommend other tests as well for diagnosing neuropathy. Those include the following:
Blood Tests
These tests can help detect increased levels of blood sugar, low levels of vitamins, and signs of metabolic issues or inflammations. All these health issues contribute to peripheral neuropathy. The testing estimates the complete blood count, which calculates different blood cells. Abnormal results can indicate vitamin B12 deficiency. It also measures the blood sugar level in the morning. By detecting the diabetes symptoms early, such as frequent urination or excess thirst, weight gain, or loss, you can manage your diabetes and prevent neuropathy issues.
Electromyography Testing
An electromyography test can help detect the problems of how your body’s nerve signals move to your muscles. The healthcare providers will apply a small needle to your muscles for this testing. Then, they will ask you to move your muscles in slow motion. A needle will help estimate the amount of electricity moving around your muscles. During this testing, you may feel like you are receiving injection shots. Sometimes, the area where the shot is injected becomes sore for some days.
Nerve Biopsy
It is the most common diagnostic technique for neuropathy tests. Research says that among the 50 patients struggling with peripheral neuropathy, nerve biopsy has altered the diagnosis in 14% of the people. It involves the removal of a slight nerve piece for a neuropathy test. Doctors perform a small incision from which a nerve sample is extracted, then sent to the lab and analyzed using a microscope. The results help identify nerve conditions, which confirms the diagnosis of neuropathy.
Skin Biopsy
Skin biopsy is a safe and painless method to diagnose neuropathy. In this diagnostic technique, healthcare providers make a small incision under anesthesia, extract a skin sample, usually from the lower leg, and send it for examination. It helps detect painful sensory neuropathy, which impacts the tiny nerve fibers known as axons. Also, it identifies other causes of neuropathy, like sarcoidosis and vasculitis. Not for all patients, but for many, skin biopsy is an effective diagnosis method compared to nerve biopsy.
Treatments For Peripheral Neuropathy
Wondering what to do after you are diagnosed with neuropathy through monofilament testing? Here are the best treatments:
-
Medications in the form of pills, slow-release medicines, injections, and patches that you can stick to your skin can treat neuropathy.
-
Surgery can securely connect cut nerves again and reduce pain caused by damaged nerves. Additionally, it helps remove defective nerves to keep transferring the nerve signals to reach the brain and vice versa.
-
Physical therapies can heal the injuries or improve symptoms of neuropathic pain. Also, it can benefit in adjusting to the changes caused by nerve damage to the nervous system by enhancing balance and preventing falls.
-
Foot care by wearing prescribed footwear as peripheral neuropathy due to diabetes generally impacts the feet. By wearing well-fitted shoes, you can prevent further complications.
Summing Up
Detecting peripheral neuropathy is essential for the patients’ effective care and overall health. That’s why monofilament testing is necessary to perform when it comes to preventing any injuries and ulcers. Doctors perform the monofilament test to check the nerve damage and any potential loss of sensation in the hands and feet. Helping the patients by healing the neuropathy-related issues is always the priority of the health professionals, and here, monofilament testing significantly benefits them.
Source link
#Monofilament #Test #Neuropathy