Diabetic Foot Ulcers can be Life-threatening
What is the prevalence rate of
diabetic foot ulcer in India and is there a study which shows any regional
disparity in the prevalence?
A. There is no nationwide study on the prevalence
rate of diabetic foot ulcers in India. However, there have been
multiple small cohort studies conducted in various places of the
country, which shows that about 20-25% patients with diabetes have
foot ulcers. It is primarily due to
poor blood sugar control and lack of awareness of
proper foot care practices. In terms of regional disparity,
the prevalence of diabetic foot ulcers may be higher among South Indians than
North Indians. It could be because of the increased number of diabetic patients
in south India.
Advertisement
Q. Why
diabetic foot ulcers do not heal?
A. That’s a very important question. There are a couple of factors
which are important for wound healing.
Firstly,blood
supply to the foot is one of the key factors for wound healing. When, one’s
blood sugar levels are not controlled for a prolonged duration, the inner lining cells of the blood vessels will
be affected, which in turn leads to atheromatous plaques and eventually blocks
the blood flow to the foot extremities. This condition is called peripheral
occlusive vascular diseases. When there is no blood supply, macro-and-micro
nutrients as well as medicines for wound healing will not reach the wound and
hence delays the wound healing process.
Secondly, about 90%
of diabetic foot wounds are infected with microbes like bacteria and fungi which
warrant culture-specific antimicrobial therapy.
Unfortunately, in rural and semi-urban as well as in
urban areas, many of the clinical practitioners do not try to find out the
bacteria growing in the wounds by culturing the wound tissue, instead, the
patients are given empirical antibiotics. These practices contributed to
increased microbial resistance to antibiotics and delayed wound healing.
Thirdly,
non-off-loading of the foot with ulcer and poor wound care. When a wound occurs
on foot, the patients must not walk with that foot, as walking would crush the
already damaged tissue and delay the healing process.
Also, the wound area must not be soaked in regular water, instead must be
cleaned with sterile solutions such as normal saline or povidone iodine as
advised by the doctor. Similarly, wound dressing must be done with sterile
dressing materials for avoiding microbial contaminations and maggots.
Fourthly,
identifying the reason for wound occurrence and appropriate treatment is
important in wound management. Inadequate clinical evaluation will mislead the
wound management plan. For example, if the foot bone is infected, then surgical
procedure of removing the infected bone ought to be done. If the wound is
malignant, wide excision or amputations may be required. If it is a vasculitic ulcer, steroid treatment may be needed.
Q. How long
does it take to heal a diabetic foot ulcer?
A. The healing of diabetic foot ulcer takes about 4 to 8 weeks,
based on all the positive conditions like blood supply, blood sugar control,
wound care, foot off-loading, appropriate medications. Other factors like
usage of sterile wound dressing materials, and ointments/lotions for wound care
depending on the nature of the wound bed as recommended by the Podiatrist.
Inappropriate wound care and non-compliance with
doctor’s instructions will prolong wound healing. I have seen a couple of
patients whose foot ulcers did not heal even after 2 years.
Q. How can
healing of ulcers be improved? Please tell us about the dressing that may be
effective
A. There are different types of ulcers and the reasons for each ulcer
development may also vary. However, wound management depends on the wound size,
depth, location and severity of the infection. In the case
of ischemic wound, which occurs due to lack of blood supply, revascularization
procedures such as peripheral angioplasty or thrombolytic therapy to treat the
blockage and improve blood supply are required
in addition to wound care. If the infection is
extending to bone (osteomyelitis),
a surgical procedure may be required. In the case of venous ulcer, the
underlying varicose vein must be treated with laser ablation or sclerotherapy.
Apart from treating the root cause of the wounds, appropriate foot care and
footwear are mandatory. As said earlier, the patient should avoid walking with the affected foot or use the
Orthoses (custom made footwear) advised by the podiatrist.
As the wounds
are of different nature, the wound dressing techniques also
vary. For example, a highly
exudative wound may need negative pressure wound therapy/vacuum therapy or adsorbant dressing. In the case of slough/biofilm on
the wound, enzymatic digestion with papain and antimicrobial local application
dressing may be required. If the ulcer is clean yet dry, then simple saline
dressing will be sufficient. Growth factors such as epidermal growth factors or
platelet-derived growth factors may also be used for
facilitating granulation and epithelialization. In general, irrespective of the
type of ulcers, wound dressing materials must be sterile. And if the dressing
material is soaked, it needs to be changed immediately.
However, it is
always wise to consult a trained wound care specialist or a podiatric surgeon
regularly as he/she would recommend dressing pattern depending upon the nature
of the wound.
Q. Can you please
tell us about recent advancement in the field of podiatry? Are there any ways
to improve blood circulation to the tiny blood vessels?
A. The branch of Podiatry has been expanding over a decade with the
advancement of research and technology. Compared to traditional wound dressing
materials, a number of modern wound dressing materials are available in the
market which augments wound healing process.
Hydrocolloid
dressing, Alginate dressing, Hydrogel dressing, semipermeable adhesive film
dressing, foam dressing, biological dressing are a
few newer dressing materials which have specific
application in wound care.
Tissue
engineered skin substitutes such as acellular and cell-containing matrices are
being used to cover partial thickness or full thickness burns. Epidermal and
dermal skin grafts are also found effective for non-healing diabetic foot
wounds and venous ulcers. Stem cell therapy is being applied for managing
ischemic and chronic non-healing wound for facilitating
new blood vessel formation, but it is not widely used due to ethical and
logistics and financial constraints. However, the long-term
benefit of stem cell therapy is yet to be documented.
Controlled drug
delivery to the wound is the other advancement in the field of Podiatry,
wherein solid nanoparticles, liposomes, microemulsions and microsponges are
being used for quick, deeper, wider or sustained delivery of medicines
into/around the wound.
Low-level laser
therapy, hyperbaric oxygen therapy and negative pressure wound therapy devices
are the other promising techniques available for wound management.
Infra-red ray
therapy and electromagnetic stimulation of cells are being found to be
effective in inducing cell proliferation, and blood circulation of the foot thereby
hastening wound healing.
The field of
Orthotics and Prosthetics is another important area which has emerged lately
with the focus on preventing foot ulcer development and
also for rehabilitating the patients who had undergone
major as well as minor foot surgeries. There are specialized insole materials
that can be placed on the footwear which will prevent undue friction and
abnormal plantar pressure. Specialized or custom made footwear is also
available which help in preventing diabetic foot ulcer.
About improving
blood circulation of the foot and legs, there are both medical and surgical
procedures available. The newer thrombolytic drugs that
are launched recently are promising for increasing blood circulation, but are
expensive. Peripheral angioplasty is the mainstay of revascularization which
has been saving many legs from major amputations of late.
Q. Are
diabetic patients who have a good control of glucose also have a higher risk
for diabetic foot ulcer?
A. Of course! All diabetic patients are at a higher risk for diabetic
foot ulcer. However, patients with good control of blood sugars from the day of
diagnosing diabetes will have relatively lower chances of foot complications
compared to the uncontrolled group. In addition to
blood sugar control, one should be very keen on
practicing proper foot care and choosing the right footwear.
Patients should care for their foot in the same way as they care their face.
Daily self-examination of their feet is inevitable as it is the easiest way to detect foot abnormality at an early stage.
Q. Are
co-morbid factors like diabetic retinopathy associated more with foot ulcers?
A. Diabetic retinopathy will affect the vision.
Hence, the chances of traumatic wounds over the feet are high. The other way of
looking at it is; for a patient who developed retinopathy which is a
microcirculation defect, would also have the small blood vessels of the foot
affected. Such microvascular defect will cause an increased
risk of foot ulcers.
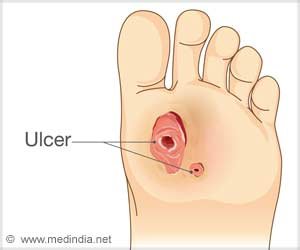
Diabetic
Foot Ulcer
People with
diabetes are at a higher risk of developing foot sores or ulcers. Diabetic foot
ulcers are a common reason for hospital stays for people with diabetes.
Diabetic ulcers are often painless, but it may take weeks or even several
months to heal. The prevalence of diabetic foot ulcer in the diabetic population
is 4 to 10 percent, and the condition is more frequent in older patients.
In diabetic
patients with neuropathy, loss of sensation in the feet leads to injuries,
which may consequently lead to foot ulceration. An untreated foot ulcer may be
infected, which may even lead to foot amputation.
If the wound
healing is slow for over two weeks, it is advisable to consult a Podiatrist.
Certain tests like peripheral angiograms, nuclear scans, x-rays, duplex scans,
tissue/pus culture and sensitivity, nutrition deficiencies should be taken to
identify the causes of delayed healing and take remedial actions.
Lifestyle
changes may help avoid diabetic foot ulcer and other complications. It is
important to quit smoking and alcohol as it may affect the blood vessels and
nerves. Constant monitoring of blood sugar level, healthy diet and medications
are important to facilitate wound healing.
Reference :
- Management of Diabetic Foot Ulcers – (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3508111/)
Source: Medindia
Source link
#Diabetic #Foot #Ulcers #Lifethreatening



